- Establishing the "Basic Safety and Disaster Prevention Policy" and Its Promotion Structure
- Data Related to Safety and Disaster Prevention
- Main Efforts for Safety, Health, and Disaster Prevention
- Safety, Health and Disaster Prevention Training
- Data Related to Safety, Health and Disaster Prevention Training
Establishing the "Basic Safety and Disaster Prevention Policy" and Its Promotion Structure
Brother Group's Basic Safety and Disaster Prevention Policy
The Brother Group has formulated the "Basic Safety and Disaster Prevention Policy" and is continuously committed to preventing disasters, injuries, and illnesses among employees and to creating a comfortable workplace by ensuring its activities comply with the OSHMS.*1
Brother Group's Basic Safety and Disaster Prevention Policy
Safety first' shall be the cornerstone of all operations. We shall try to create a comfortable working environment that allows all our associates to feel safe and work in good health. Safety culture shall be established at the same time.
Regulations of System and Control for Disaster Prevention of the Brother Group
In December 2017, the Brother Group established the "Regulations of System and Control for Disaster Prevention of the Brother Group" to ensure the safety of employees and workplaces when a fire breaks out.
These regulations are composed of three sections: (1) "fire prevention management" to take precautions against fires; (2) "firefighting management" to minimize damage from fires; and (3) "personal safety management" to ensure the safety of employees. In April 2021, we added the "clause on precautions regarding high fire risk equipment, work, etc. regarding firefighting equipment etc."
The Brother Group has applied these regulations to its main facilities in and outside Japan.*2
- The OSHMS, the initialism for the Occupational Safety and Health Management System, is a safety and health management system established by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare with the aim of improving the safety and health standards of workplaces.
- Scope of Application
Japan: BROTHER INDUSTRIES, LTD., NISSEI CORPORATION, MIE BROTHER PRECISION INDUSTRIES, LTD., BROTHER LOGITEC LTD., BROTHER ENTERPRISE, LTD.
Overseas: BROTHER TECHNOLOGY (SHENZHEN) LTD., ZHUHAI BROTHER INDUSTRIES, CO.,LTD., BROTHER INDUSTRIES (VIETNAM) LTD., BROTHER INDUSTRIES (PHILIPPINES), INC., BROTHER MACHINERY XIAN CO., LTD., TAIWAN BROTHER INDUSTRIES, LTD., BROTHER INDUSTRIES SAIGON, LTD., BROTHER MACHINERY INDIA PRIVATE LTD.
Safety and disaster prevention promotion structure
Establishment of the Central Safety, Health and Disaster Prevention Committee
Brother Industries, Ltd. (BIL) has established the Central Safety, Health, and Disaster Prevention Committee composed of the Officers of the group facilities in Japan. The Committee is chaired by the Safety, Health, and Disaster Prevention Officer of BIL.
Conducting regular audits
At the Brother Group's main manufacturing facilities outside Japan, the Workplace Safety and Disaster Prevention Group of BIL's Human Resources Department, which acts as the secretariat of the Central Safety, Health, and Disaster Prevention Committee, conducts regular audits to increase the level of safety, health, and disaster prevention and develop local staff.
ISO45001 certification status
Some manufacturing facilities, including Brother Industries (Vietnam) Ltd. and Brother Industries (Philippines), Inc., have been externally certified under ISO 45001. About 8% of the Brother Group facilities had obtained this certification as of March 31, 2025.
Data Related to Safety and Disaster Prevention
Targets/Achievements
Serious accidents at Brother Group facilities*1
| FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 | FY2025 | FY2026 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targets | 0 | (Three-year target) | (Three-year target) | ||||
| Achievements | 0 | 0 | 1*2 | 0 | 0 | - | - |
- Fatal accidents, accidents resulting in hospitalization of 30 days or more, and accidents resulting in permanent injuries
- Please refer to the following link for details on the recurrence prevention measures implemented in response to the serious accident that occurred, as part of Domestic efforts to prevent accidents
Data Related to Safety and Disaster Prevention
| FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of fatal occupational injuries*3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Frequency rate of lost-time occupational injuries*4,5 | 0 | 0.27 | 0 | 0 | 0.14 |
| Frequency rate of lost-time occupational illnesses*3,5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Number of lost-time occupational injuries (one day or more)*3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
*3: Brother Industries, Ltd.
*4: Number of lost-time deaths and injuries from work-related accidents/Total number of working hours x 1,000,000
*5: Number of lost-time illnesses from work-related accidents/Total number of working hours x 1,000,000
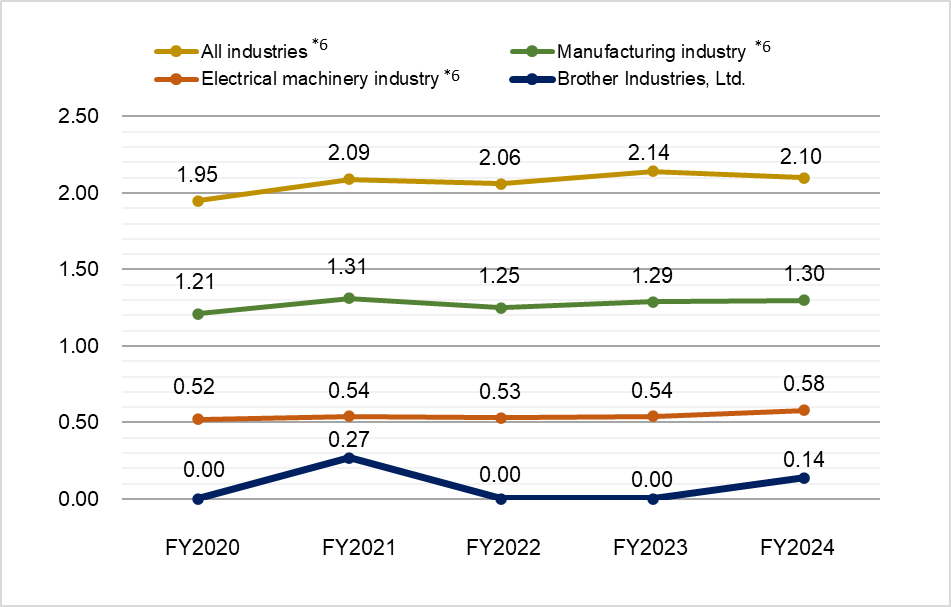
*6: Source: Survey on industrial accidents provided by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan
Number of occupational injuries reported and yearly incident rate at main manufacturing facilities outside Japan (lost-time injuries and non-lost time injuries)*7
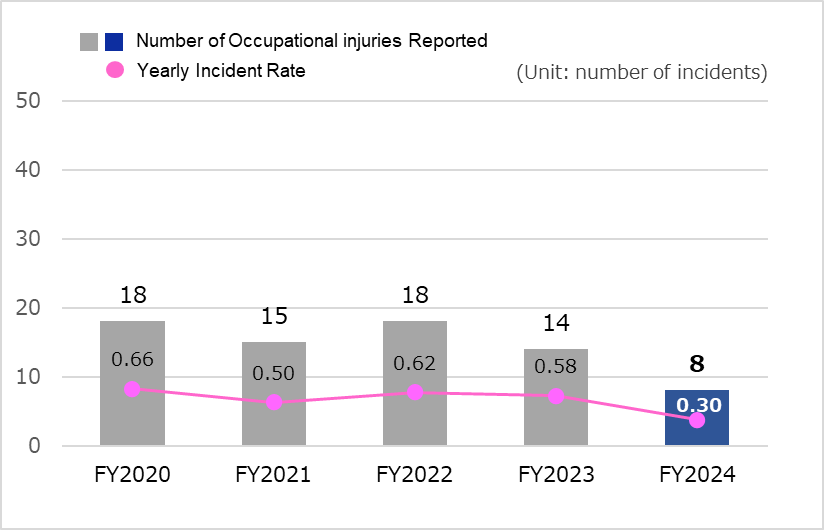
*7: Yearly incident rate: (number of incidents/number of employees) × 1,000
Results related to safety and disaster prevention at major manufacturing facilities including overseas*8
| FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency of worker injuries (number of injuries per hour worked)*9 | 0.33 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.33 | 0.16 |
| Occupational accident rate (number of injuries per worker)*10 | 0.0007 | 0.0007 | 0.0007 | 0.0007 | 0.0004 |
*8: Main manufacturing facilities including overseas
BROTHER INDUSTRIES, LTD., BROTHER TECHNOLOGY (SHENZHEN) LTD., ZHUHAI BROTHER INDUSTRIES, CO., LTD., BROTHER INDUSTRIES (VIETNAM) LTD., BROTHER INDUSTRIES (PHILIPPINES), INC., BROTHER INDUSTRIES (U.S.A.) INC., BROTHER INDUSTRIES (U.K.) LTD., BROTHER INDUSTRIES (SLOVAKIA) s.r.o., BROTHER MACHINERY XIAN CO., LTD., TAIWAN BROTHER INDUSTRIES, LTD., BROTHER INDUSTRIES SAIGON, LTD.
*9: Frequency of worker injuries (number of injuries per working hour): Number of injuries due to occupational accidents/Total number of actual working hours X 1,000,000
*10: Occupational accident rate (number of injuries per worker): Total number of injuries due to occupational accidents/Total number of workers
Main Efforts for Safety, Health, and Disaster Prevention
Domestic efforts to prevent accidents
To reduce potential occupational injuries, BIL is striving to improve the work environment so as to prevent accidents by taking the following measures:
| Potential occupational injuries | Measures |
|---|---|
| Fall from a height |
|
| Machinery-related caught-in or -between accidents |
|
| Forklift collision accident |
|
| Chemical burns |
|
Recurrence prevention of serious accidents
BIL conducts risk assessments during machine operation and work activities, as well as hazard prediction training, to improve workplace safety and raise employee safety awareness. In addition, BIL implements various initiatives to prevent the recurrence of serious accidents.
In FY2022, a serious accident occurred at a Brother Group manufacturing facility when a production worker, attempting to fix a malfunctioning machine, inserted their hand into the running machine and suffered fingertip amputation. As a recurrence prevention measure for this accident, the movable cover on the moving part of the relevant machine and of similar machines was replaced with a fixed one to prevent hands from entering while the machine is operating. In addition, production workers were re-educated to stop machine operation and notify management when a machine malfunctions and to wait for the malfunction to be resolved before resuming work.
Recurrence prevention of occupational accidents
BIL is committed to preventing occupational accidents and to promoting recurrence prevention measures in response to work-related injuries.
In FY2023, an accident occurred during a chemical filtration task when chemicals splashed and entered a worker's eye. As a recurrence prevention measure, the equipment involved in the accident was replaced, and workers received additional training on safety procedures, particularly strict adherence to personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements. Furthermore, to prevent similar incidents, this case was introduced in an e-learning program in FY2024, and other examples of tasks that require PPE use were shared, in addition to filtration work. In FY2024, another accident occurred in which a worker lost balance on a staircase landing and fractured their ankle. In addition, in response to multiple slip-and-fall accidents during commuting in recent years, safety alerts were issued to employees through each site's Safety and Health Committee. Furthermore, a physical training workshop was held with an external instructor to help employees build strength and prevent slip-and-fall accidents.
Promoting Safety, Health, and Disaster Prevention Activities Globally
Checking workplace safety, health and disaster prevention situation
At each of our major manufacturing facilities, both in Japan and overseas, the Safety, Health, and Disaster Prevention Committee members regularly patrol the facilities. If any problems are found, they are quickly resolved. In addition, for facilities where the work environment has changed significantly, such as major changes to production lines, the situation of workplace safety, health, and disaster prevention is checked through patrols by the Chairperson of the Central Safety, Health, and Disaster Prevention Committee.
Global dissemination and sharing of information about past disasters and safety and disaster prevention activities
The Brother Group shares information about occupational accidents occurring at its main manufacturing facilities in and outside Japan and countermeasures against them on its intranet and other devices to make such information available at all group facilities. Each facility applies these countermeasures to its workplaces in order to prevent the same or similar accidents from occurring.
At the Brother Safety and Prevention Convention held annually, manufacturing facilities that have engaged in excellent safety and disaster prevention activities are awarded, and case studies of the awarded manufacturing facilities are presented to share information among other facilities. In FY2024, the convention was held in Japan, bringing together relevant parties from facilities around the world to share best practices in safety and disaster prevention activities.
Conducting risk management for operations and equipment
At the Brother Group, it is required to perform an assessment of the risks associated with operations and equipment when installing equipment to take on a new project, when a change has been made to the work location or raw materials, or when there are changes to work methods, such as changes to the tools used or the assembly sequence. This risk assessment identifies potential hazard sources,*1 such as those resulting in falls, being caught in or between objects, electric shocks, explosions, and fires, striving not to overlook any important hazard sources. Moreover, the assessment identifies other sources that might exist in each work process and evaluates their risk levels to enable appropriate measures to be taken for each level. In addition, the degree of such hazards of equipment is visualized if it is judged to have residual hazards above a certain level even after safety measures based on a risk assessment are taken.
After a certain period of time*2 has passed since conducting a risk assessment, we will recheck to see if there have been any changes to operations, risks, or the like. In the event of any changes, we conduct a risk assessment again.
- The causes of risks and the root causes of accidents
- 3 years, as a guide
Safety, Health and Disaster Prevention Training
Safety and Health Education
To ensure safety and health, BIL annually provides risk prediction training, safety and health education, and so forth for each facility based on the plans formulated at the Safety, Health, and Disaster Prevention Committee. As for the education, BIL offers e-learning training for all BIL employees. In FY2024, 4,251 employees, which represented 94.8% of the intended participants, took the training. BIL also conducts an educational session for new employees every April. In FY2025, this session was held with 108 new employees, the full participation of the intended participants. For mid-career recruits or newly-hired temporary employees, BIL holds educational sessions every month. The sessions held in FY2024 had 110 employees, involving all of the intended participants.
In addition, BIL also provides training tailored to the specific needs of each operation. For example, employees engaged in specialized work involving the handling of chemical substances are provided training tailored to their tasks. Employees who drive company vehicles are required to take traffic safety courses under a permit system. For the facilities outside Japan, training is provided for new and mid-career recruits at each location.
Safety and Disaster Prevention Training
Regarding preparation for disasters, BIL has been making efforts to minimize damage caused by possible disasters at its respective facilities. Such efforts include the consolidation of disaster prevention organizations, evacuation drills, initial firefighting training, and lifesaving training using an AED (automatic external defibrillator), and the legal inspection of fire protection equipment.
In 2007, BIL concluded a memorandum of understanding on support and collaboration in the event of a large-scale disaster with its local community through the mediation of a local administrative body. In addition, since 2014, BIL has been conducting evacuation drills jointly with a neighboring nursery school with which BIL signed a memorandum.
Since 2016, BIL has been conducting training for setting up a disaster headquarters at its head office.
Raising disaster prevention awareness
In response to the Nankai Trough Earthquake Extra Information (Advisory) issued on August 8, 2024, BIL conducted an emergency e-learning session to raise employees' disaster preparedness awareness and enhance their ability to respond in the event of an earthquake.
The session covered the company's response policy, appropriate actions employees should take in response to a major earthquake, and the company's earthquake preparedness measures. A total of 4,025 employees, accounting for 92.7% of those targeted, received the training.
Data Related to Safety, Health and Disaster Prevention Training
| FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of participants in safety training (e-learning) based on BIL's internal regulation on safety and health education procedures | 3,802*2 | 3,959*2 | 4,052*2 | 4,183 | 4,251 |
| Number of participants in disaster prevention training (e-learning) based on BIL's internal regulation on safety and health education procedures | 4,250 | 4,025 | |||
| Number of participants in other safety and disaster prevention training (e-learning) based on BIL's internal regulation on safety and health education procedures*3 | 2,723 | 3,253 | 3,843 | 4,415 | 4,502 |
- Including incoming seconded employees, temporary employees, and fixed-term employees
- Safety education and disaster prevention training have been provided together
- Since FY2019, the number of participants has included those in mental health-related education

